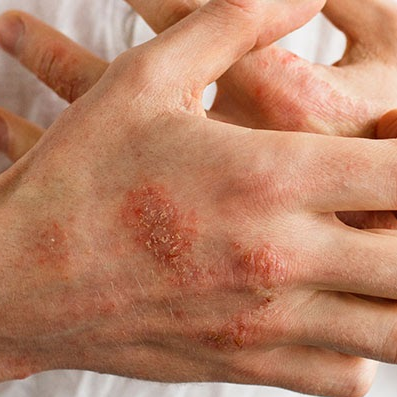
Eczema (Skin eczema) is a skin condition characterized by patches of inflamed, cracked, rough skin that may itch or develop blisters. Eczema is not contagious and can be triggered by specific foods like nuts and dairy or environmental factors such as smoke, pollen, certain soaps, and fragrances.
Eczema is typically mild, and its common symptoms include dry and scaly skin, redness, itching, and open sores, which may vary between children and adults. Most people with this condition develop it before the age of 5, and in 60% of cases, symptoms subside by adolescence. Symptoms may flare up periodically and then improve or disappear entirely. Although there is no cure for eczema, many home remedies can help manage symptoms and provide relief.
Treating Eczema at Home
1- Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera gel, extracted from the leaves of the aloe plant, is widely used to treat various conditions, including eczema. It has antibacterial, antimicrobial, immune-boosting, and wound-healing properties. Its antibacterial and antimicrobial benefits can prevent skin infections often caused by dryness and cracking, while its wound-healing properties soothe damaged skin.
It is best to use gel directly from the plant or products free from preservatives, alcohol, fragrances, and dyes, as these can further irritate sensitive skin. Test a small amount on your skin first to check for allergies before using it.
2- Apple Cider Vinegar
Although the acidic nature of apple cider vinegar may harm soft skin, it is reported to aid in improving eczema.
Apple cider vinegar balances skin acidity
Skin is naturally acidic, but individuals with eczema may have lost some of this acidity, weakening its defenses. Diluted apple cider vinegar can help restore this balance, but undiluted vinegar may cause burns. Many soaps and detergents, being alkaline, strip the skin's acidity and increase its vulnerability, exacerbating eczema.
Apple cider vinegar fights bacteria
Studies show that apple cider vinegar combats bacteria and helps prevent skin infections. Mix one tablespoon of vinegar with one cup of warm water, apply with a cotton ball or gauze, cover with a clean cotton cloth, and leave for three hours. Alternatively, add two cups of vinegar to a warm bath, soak for 15–20 minutes, rinse thoroughly, and moisturize immediately after drying.
3- Bleach
Though it may sound risky, research indicates that bleach, due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, reduces eczema symptoms.
Use regular bleach with a 6% concentration, adding half a cup to a bathtub of water or one teaspoon to a gallon of water. Soak for 5–10 minutes, rinse thoroughly with warm water, and gently dry. Use lukewarm water to prevent dryness, and moisturize immediately after drying. Do not use bleach if it causes discomfort, redness, or irritation, or if you have asthma or respiratory issues.
4- Oatmeal
Oatmeal-based lotions have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that relieve dryness, roughness, and itching.
Add oatmeal to a warm bath to help repair your skin. Oatmeal lotions and creams are also available. Oatmeal is generally safe for all ages, but avoid it if you are allergic to oats or gluten.
5- Bathing
People with eczema need extra skin moisture, and bathing provides it. Proper bathing is essential for eczema treatment; otherwise, it can worsen symptoms. Avoid very hot or cold water, unsuitable soaps, over-washing, and skipping post-bath moisturizing. Follow these guidelines:
- Bathe at least once a day.
- Use lukewarm water.
- Limit baths to 10–15 minutes.
- Avoid scrubbing the skin.
- Use non-irritating cleansers instead of soap.
- Gently pat the skin dry and moisturize within three minutes of drying.
6- Coconut Oil
Coconut oil contains healthy fatty acids that moisturize and soothe dry, eczema-prone skin. Apply it after bathing and several times throughout the day. You can also use it overnight. Solid at room temperature, it liquefies upon contact with skin. Avoid coconut oil if you are allergic to coconuts.
7- Honey
Honey is a natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent that has been used for wound healing for centuries. It helps heal wounds, boost immune function, and combat infections. Applying honey to eczema moisturizes and repairs the skin while preventing infections. Manuka honey, derived from a plant in New Zealand, is especially effective.
8- Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil, derived from the leaves of the Melaleuca alternifolia tree native to Australia, is commonly used for skin issues, including eczema. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and wound-healing properties that relieve dryness, itching, and infection. Mix it with almond or olive oil before applying.
9- Diet Changes
Eczema is an inflammatory condition that causes redness and sores. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods like fish, leafy greens, fruits, beans, lentils, turmeric, and cinnamon can reduce inflammation. Avoid or limit inflammatory foods like dairy, eggs, soy, and wheat.
10- Mild Soaps and Detergents
Chemicals in laundry detergents can aggravate eczema, but using gentle, fragrance-free products minimizes irritation. Avoid leaving fabric softener on clothes, as its chemicals and fragrances can irritate the skin. Use mild soaps and cleansers instead of alkaline ones.
11- Avoid Extreme Heat
Sitting near heaters or fireplaces and exposure to warm, dry air dehydrates the skin and worsens eczema symptoms. Use a humidifier during dry months and avoid close proximity to heat sources.
12- Protect from Cold Weather
Cold, harsh winter winds dry out the skin and trigger eczema. Cover your skin and stay warm during cold weather.
Home Remedies for Infants and Children
Many home remedies are safe for infants and children, but consult a doctor before trying them.
- Avoid dressing children in heavy clothing, as sweating can worsen eczema and cause rashes and itching.
- Use mittens to prevent babies from scratching their skin.
- Apply gentle moisturizers, avoiding the eyes and nose.
- Consult a doctor before using apple cider vinegar or bleach.
- Oatmeal baths are safe for children but should not contact the eyes.
- Avoid excessive washing; most children need only one or two baths weekly to prevent dry skin.
- Use alcohol- and fragrance-free wipes with soothing ingredients like aloe vera.
- Choose eczema-specific shampoos for children.
There is no definitive cure for eczema, but home remedies can help control and alleviate symptoms. If eczema becomes severe or unresponsive to home treatments, seek medical advice.











Our Customers' Comments
No comments registered