Any physical injury caused by severe blows to the skin is referred to as a wound. These blows, especially when caused by sharp objects, can result in tearing and deep tissue damage. If the impact is severe, it may also damage bones or tissues between the skin and bone, leading to fractures.
Types of Wounds
- Pressure sores caused by immobility or old age.
- Vascular wounds, including venous and arterial ulcers.
- Diabetic wounds, typically affecting the feet.
- Surgical wounds, such as reopened stitches.
- Gunshot wounds caused by bullet impacts.
- Burn wounds.
- Wounds caused by crushing, punctures, abrasions, and tears.
Certain injuries, specific conditions, and even small cuts can result in bleeding. This may initially cause fear and anxiety. Regardless of the cause of the bleeding, the first step is to remain calm and focus on stopping the bleeding. As quick action is crucial, some home remedies can help clot the blood and rapidly stop the bleeding.
If bleeding is caused by animal bites, a deep wound, or injuries to the face, and the bleeding doesn’t stop after 15 to 20 minutes, the individual is experiencing severe bleeding. Symptoms of shock, such as cold and clammy skin, weak pulse, dizziness, weakness, rapid heartbeat, or loss of consciousness, should also be checked.
In some cases, blood loss may lead to light-headedness or nausea. Below are some home remedies to stop bleeding quickly. If these remedies do not resolve the wound, consult a specialist dermatologist. You can also ask your wound-related questions via online consultation on Pezeshkbook.
Home Remedies for Quickly Stopping Bleeding
- Apply pressure and elevate the injured area.
- Ice Compress
- Tea
- Yarrow
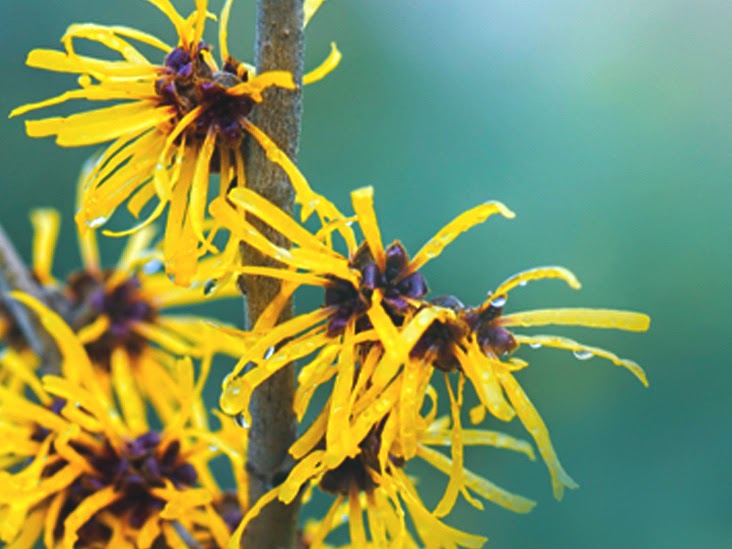
- Witch Hazel
- Zinc Tablets and Vitamin C Powder
- Petroleum Jelly
- Antiperspirant
- Mouthwash
Help the individual stay calm. If the cut is large and the bleeding is severe, ask them to lie down and remove debris such as wood or grass from the wound. If it’s a small cut, wash it with soap and water, but avoid cleaning large wounds.
To stop the bleeding, firmly press on the wound with your hand and, if possible, elevate the injured area above the heart. Use a clean cloth or sterile gauze to do this. If no clean cloth is available, any fabric can be used—even if it’s not sterile—for applying pressure.
If blood soaks through the cloth or gauze, do not remove it, as this may disrupt clot formation and restart the bleeding. Instead, add another cloth or gauze layer on top and continue applying pressure.
Maintain pressure for 5 to 10 minutes initially. If the bleeding hasn’t stopped, continue for another five minutes. If bleeding persists, seek emergency medical help or contact your doctor. Once the bleeding has stopped, gently clean the area with warm water and soap. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or iodine, as they can damage tissue.
Applying an ice compress to a bleeding area—especially in the mouth—is an effective home remedy. Ice helps reduce swelling and shortens bleeding time. Wrap the ice in a clean cloth or gauze and never apply it directly to the wound. Avoid using ice if the individual’s body temperature is abnormally high or low.
A common remedy to stop bleeding, especially after dental procedures, is using a damp tea bag on the injured area. Tannins, the chemicals in tea responsible for its bitter taste, help clot blood.
Studies show that green tea is the most effective for blood clotting. Individuals who used gauze soaked in green tea extract on a bleeding tooth experienced less bleeding and discharge.
Herbal teas without caffeine or tannins are ineffective for treating bleeding. Gently bite down on the tea bag or hold it in place for at least 30 minutes.
Yarrow, a plant belonging to the Achillea family, is known for stopping bleeding. To use, grind dried yarrow into a powder or cover the wound with fresh yarrow leaves and flowers. While pressing on the wound, keep the injured area elevated above the heart.
Witch hazel helps stop bleeding from small cuts and nail injuries. It tightens the skin, reduces blood flow, and promotes clotting. Apply pure witch hazel to gauze and press it onto the wound. Pure witch hazel, free of additives and alcohol, is available in pharmacies and is effective for certain skin conditions. Other helpful plants include horsetail, plane tree, and rose.

A combination of vitamin C powder and zinc lozenges can help clot blood during prolonged bleeding, especially after tooth extractions. Sprinkle vitamin C powder directly onto the wound and place a zinc tablet in the mouth. Bleeding typically stops, and a clot forms within three minutes.
Petroleum jelly, made from oil and wax to protect the skin, can be used to stop minor cuts and shallow wounds. Ensure the wound is dry and clean before applying petroleum jelly to avoid leaving residue after the bleeding stops.
Aluminum chloride, a chemical in antiperspirants, not only reduces sweating but also constricts blood vessels and helps clot minor external bleeding.
The alcohol in mouthwash can aid blood clotting. In addition to regular mouthwash, aminocaproic acid (Amicar) is used to treat oral bleeding after dental work. Amicar is also used to manage bleeding episodes in conditions like aplastic anemia, liver cirrhosis, and certain pregnancy complications. To stop oral bleeding, gargle gently with the liquid to promote quick clotting.
Most minor bleeding can be stopped at home with simple remedies. Once bleeding stops, consult a doctor for severe injuries to:
- Suture the wound if necessary.
- Properly clean the wound.
- Examine for internal bleeding, shock, or signs of infection.
Uncontrolled bleeding is one of the leading causes of trauma-related death, but it is largely preventable. Knowing how to stop and manage bleeding is crucial.
Sources: healthline.com, webmd.com, medicalnewstoday.com











Our Customers' Comments
No comments registered