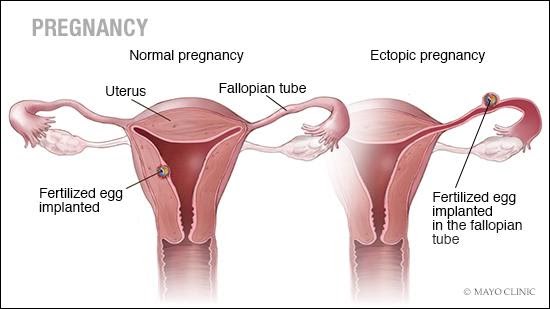
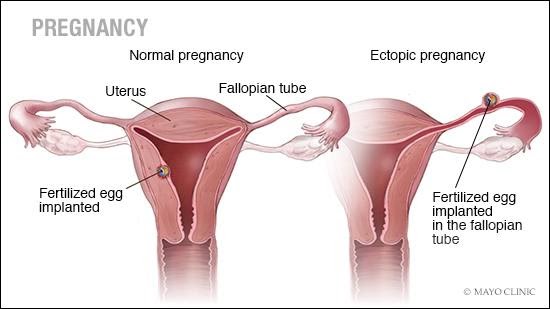
Pregnancy in a woman's body from fertilization to childbirth requires several stages. One of these stages is when the fertilized egg moves towards the uterus for implantation. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg does not attach to the uterus and may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix. While a pregnancy test might show a positive result, the fertilized egg cannot grow properly outside the uterus. Approximately one in 50 pregnancies results in an ectopic pregnancy. If untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can become a medical emergency, but timely treatment reduces the risk of complications and increases the chances of future healthy pregnancies.
What Causes Ectopic Pregnancy?
The cause of ectopic pregnancy is not always clear. In some cases, the following conditions are associated with ectopic pregnancy:
- Inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes due to a previous disease, infection, or surgery
- Hormonal factors
- Genetic abnormalities
- Birth defects
Your doctor can certainly provide more specific information about your situation.
Who Is at Risk for Ectopic Pregnancy?
All women are at risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following:
- Mother aged 35 or older
- History of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple miscarriages
- History of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- History of endometriosis
- Pregnancy with the help of fertility drugs or methods
- Smoking
- History of ectopic pregnancy
- History of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- Having structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that make it difficult for the egg to move.
If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor. To minimize the risk of ectopic pregnancy in the future, you can consult with a fertility specialist.
What Are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Nausea and breast pain are common symptoms in both ectopic pregnancy and regular pregnancies. The following symptoms are more commonly seen in ectopic pregnancy and may indicate a medical emergency:
- Sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- Severe pain on one side of the abdomen
- Spotting or vaginal bleeding (from mild to severe)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rectal pressure
If you are pregnant and experience any of these symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
If you suspect you have an ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor immediately. Ectopic pregnancy cannot be diagnosed through a physical exam. An ultrasound, particularly a transvaginal ultrasound, is required for diagnosis.
Your doctor may also use blood tests to determine levels of hCG and progesterone. These are hormones present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay stable over a few days, and no pregnancy sac is visible on the ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic. If there are severe symptoms such as significant pain or bleeding, there may not be enough time to perform all these steps. This is because, in severe cases, the fallopian tube may rupture and cause severe internal bleeding. In such cases, your doctor may perform emergency surgery for immediate treatment.
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is not safe for the mother. It is essential that the pregnancy be removed as soon as possible for the immediate health of the mother and long-term fertility. Treatment options depend on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its growth.
Medication Treatment for Ectopic Pregnancy
Your doctor may prescribe several medications if immediate complications are unlikely. One common drug is methotrexate (Rheumatrex). Methotrexate is a medication that stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells in the ectopic mass. If you are taking (injecting) this drug, you will need to have regular blood tests to ensure the drug is working. It is considered effective when symptoms similar to a miscarriage, such as cramping, bleeding, and passing tissue, are observed.
In this case, further surgery is rarely needed. Methotrexate does not carry the risks of fallopian tube damage that are associated with surgery. However, after taking this medication, you cannot become pregnant for several months.
Surgical Treatment for Ectopic Pregnancy
Many surgeons recommend removing the pregnancy and repairing any internal damage. This method is called laparoscopy. The doctor inserts a small camera through a small incision, then removes the pregnancy and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube. If surgery is unsuccessful, the surgeon may repeat the laparotomy (this time with a larger incision). If damaged, the doctor may need to remove the fallopian tube during surgery.
Home Care for Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Your doctor will provide specific instructions on how to care for your incisions after surgery. The main issue is to keep the incisions clean and dry during recovery and to check them daily for signs of infection, which may include the following:
- Persistent bleeding
- Excessive bleeding
- Foul-smelling discharge from the surgical area
- Feeling of heat
- Redness
- Swelling
After surgery, some vaginal bleeding and small blood clots are normal. This can happen for up to six weeks after the procedure. Other self-care actions to take include:
- Do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds (4.5 kg).
- Drink plenty of fluids to prevent constipation.
- Rest your pelvis, which means avoiding sexual intercourse, tampon use, and douching.
- Rest as much as possible during the first week after surgery.
If the pain increases or you notice any abnormal symptoms, notify your doctor.
Prevention of Ectopic Pregnancy
Prevention and prediction are not always possible. However, ask your partner to use condoms during sex and limit the number of sexual partners. This reduces the risk of sexually transmitted diseases, which can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes.
Regular checkups with your doctor, including routine gynecological exams and screenings, are important. Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a preventive measure.
Long-term Outlook After Ectopic Pregnancy
The long-term outlook after an ectopic pregnancy depends on the extent of physical damage. Most people who have had an ectopic pregnancy will have a healthy pregnancy in the future. If both fallopian tubes (or even just one) are still healthy, the egg can be fertilized naturally. However, if you have a pre-existing fertility problem, this may affect your future fertility and increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. This is particularly true if previous fertility problems have led to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery may cause scarring in the fallopian tubes, which can lead to future ectopic pregnancies. If one or both fallopian tubes need to be removed, discuss potential fertility treatments with your doctor. One option is in vitro fertilization (IVF), which involves implanting a fertilized egg into the uterus.
Remember that many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies. When you are ready, discuss healthy pregnancy options for the future with your doctor.












Our Customers' Comments
No comments registered